Riveting Gun: Precision Joining for Modern Manufacturing
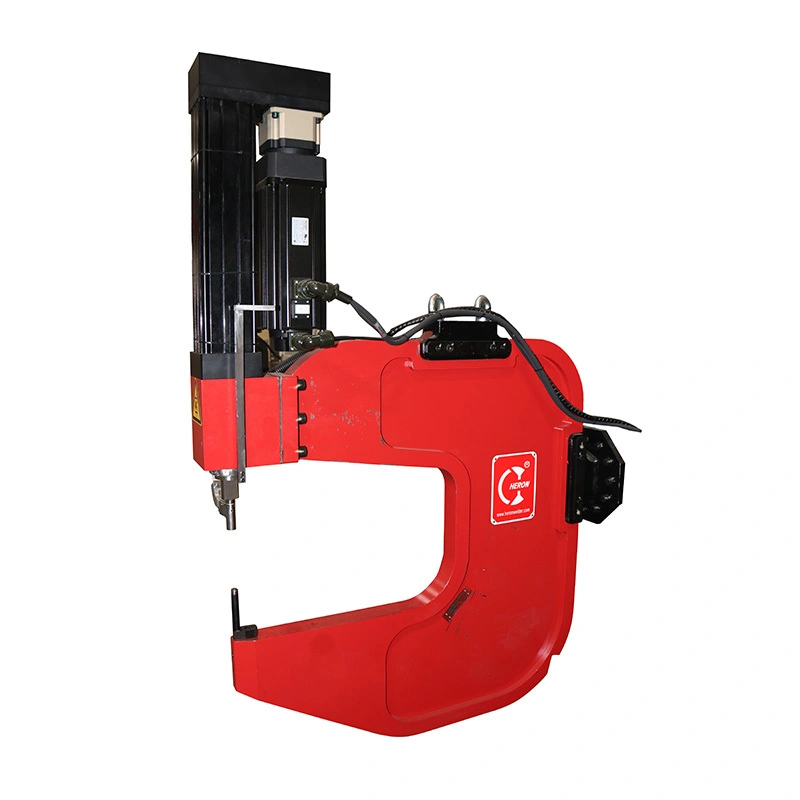

In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, efficient and reliable joining technologies are essential for product quality, throughput, and cost control. Among these, the riveting gun stands out as a versatile tool for high-strength mechanical joining across automotive, appliance, aerospace, electronics, and fabricated metal assemblies. This article explores the principles, applications, advantages, and best practices around riveting guns—positioning Heron Welder as your expert partner for rugged, high-performance riveting solutions.
What Is a Riveting Gun?
A riveting gun is a powered installation tool designed to set fasteners—typically blind rivets, blind rivet nuts (Nutserts®/rivnuts), structural rivets, or specialty rivets—into assemblies where traditional access from both sides isn’t possible. Using pneumatic, hydraulic, electric, or electro-pneumatic actuation, these tools deliver controlled force to deform and seat the rivet securely.
Unlike manual hand tools, industrial riveting guns provide repeatable force and precise control, enabling consistent joint quality across high volumes. They can be handheld, robotic-mounted, or integrated into automated production lines.
Core Components and Operating Principles
1. Actuation Systems
The driving mechanism sets industrial riveting guns apart in performance and application:
-
Pneumatic Riveting Guns: Use compressed air for rapid cycling and consistent force—ideal for high-rate assembly with moderate force requirements.
-
Hydraulic Riveting Guns: Offer high force with smooth, controlled motion—suited for large structural rivets or thicker materials.
-
Electric / Electro-Pneumatic Systems: Combine precision control with energy efficiency, often integrated with CNC or PLC controllers for advanced automation.
2. Nosepieces & Mandrels
The nosepiece holds the rivet and aligns it with the joint. Interchangeable nosepieces accommodate different rivet diameters and styles. Mandrel capture and ejection systems minimize downtime and improve operator safety.
3. Force & Stroke Control
Precision riveting guns from Heron Welder incorporate adjustable stroke and force control to match specific rivet types and material stacks. This capability ensures optimal swage profiles and minimizes material distortion.
Why Choose Riveting Guns in Industrial Manufacture?
Enhanced Joint Strength and Reliability
Riveting guns produce high-integrity, vibration-resistant joints—critical for safety-sensitive applications like automotive chassis, rail car bodywork, and structural assemblies in consumer electronics.
Accessibility and Blind-Side Joining
When one side of the workpiece is inaccessible, riveting guns excel. Blind rivets can be set from a single side, enabling joining in complex assemblies or closed structures.
Cycle Time and Productivity
Powered riveting guns reduce manual effort and substantially improve cycle times over handheld manual tools. In automated configurations, they execute consistent operations with minimal human intervention.
Integration with Automation
Riveting guns can be robot-mounted or integrated into automated cells with vision systems, track feeders, and PLC controls—facilitating unattended production and traceable quality.
Common Industrial Applications
Automotive & Transportation
-
Body-in-White Assembly: Structural blind rivets join steel, aluminum, and hybrid material stacks.
-
Interior Trim & Components: Fast, reliable joining for door panels, consoles, and brackets.
-
Electrical Shielding & Cable Trays: Blind rivet nuts provide threaded attachment points.
Appliances & Consumer Goods
Riveting guns secure garment components, housings, and internal frameworks with high repeatability and low rebound.
Aerospace & Defense
Lightweight assemblies demand precision joining with minimal material stress. Electric or hydraulic riveting guns deliver controlled force profiles suitable for advanced alloys.
Electronics & Enclosures
Small-format rivets and rivet nuts produce strong joints in sheet metal, enclosures, and mounting frames without risk of damaging delicate internals.
Riveting Gun vs. Alternative Joining Methods
Riveting Gun vs. Welding
| Feature | Riveting Gun | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Input | Cold process | Generates heat; potential distortion |
| Material Compatibility | Dissimilar materials easily joined | Some combinations difficult |
| Skill Requirement | Lower; repeatable | Higher; weld certification |
| Cycle Time | Fast | Variable |
| Access | Blind-side capable | Often requires full access |
Riveting guns avoid heat-affected zones, making them ideal where thermal distortion or electrical conductivity change is unacceptable.
Riveting Gun vs. Threaded Fasteners
While bolts and screws provide disassembly, riveting guns with blind rivet nuts deliver permanent, vibration-resistant threads in thin sheet metal where tapping isn’t feasible.
Riveting Gun vs. Adhesive Bonding
Adhesives offer seamless joints but require surface prep and cure time. Riveting guns provide immediate strength without secondary process waits.
Selecting the Right Riveting Gun
Evaluate Your Fastener Type
Consider rivet size, material, and style (open sleeve, closed end, structural, sealing). Heron Welder offers tooling solutions matched to a wide fastener range.
Match Force to Material Stack
Harder materials and multi-layer stacks demand higher force. Pneumatic systems excel in throughput; hydraulic or electro-pneumatic guns deliver high, controlled clamp force for structural work.
Consider Automation Needs
For high volumes, choose riveting guns with electronic control interfaces, integrated sensors, and feedback for PLC/robotic cell integration.
Ergonomics and Operator Experience
For semi-manual lines, select lightweight, well-balanced riveting guns with reduced recoil and easy mandrel handling to minimize fatigue.
Best Practices for Riveting Gun Implementation
Standardize Fastener Specifications
Maintain consistency in rivet types and sizes across similar assemblies to streamline tooling and reduce changeover time.
Maintain Clean Tooling
Contaminants and wear can affect stroke accuracy and joint quality. Establish routine maintenance schedules for nosepieces, mandrels, and seals.
Integrate Quality Monitoring
Use force or displacement sensors to verify each joint. Feedback systems can detect incomplete swages and trigger alerts or part rejection.
Train Operators and Integrators
Even with automation, understanding basic riveting principles and tool limits ensures better decision-making and reduces downtime due to misuse.
Why Partner with Heron Welder?
Heron Welder has decades of industrial joining expertise delivering robust riveting guns and integrated automation solutions tailored to complex manufacturing environments. Our product line spans:
-
High-performance riveting guns with pneumatic, hydraulic, and electric actuation
-
Custom nosepieces and tooling sets for a broad range of fasteners and joint configurations
-
Automated riveting stations with PLC integration, force feedback, and robotic compatibility
-
Application support and engineering consultation to optimize joint design, cycle time, and total cost of ownership
We understand that choosing the right riveting technology impacts product integrity, assembly throughput, and long-term reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What types of rivets can a riveting gun install?
Riveting guns can install blind rivets, structural rivets, blind rivet nuts, sealing rivets, and specialty fasteners across materials like aluminum, steel, stainless, and composites.
2. Can riveting guns be automated?
Yes—riveting guns are commonly integrated with robotic arms or fixed automation cells controlled via PLCs, with options for force monitoring and error detection.
3. What’s the difference between pneumatic and hydraulic riveting guns?
Pneumatic guns use compressed air for rapid cycling, while hydraulic guns provide smoother, higher force for larger rivets and thicker stacks.
4. Are riveting guns suitable for dissimilar materials?
Absolutely. Riveting guns join different materials without heat distortion, making them excellent for mixed metal assemblies.
5. How do I know which riveting gun is right for my application?
Factors include fastener type, material stack, cycle rate, access constraints, and automation level. Heron’s application engineers can help specify the ideal solution.
Ready to Optimize Your Assembly Process?
Whether you’re evaluating riveting guns for a new production line, upgrading existing equipment, or integrating automation, Heron Welder delivers tailored solutions with performance and reliability. Request a quote or consult our engineering team today to elevate your manufacturing with precision joining technology