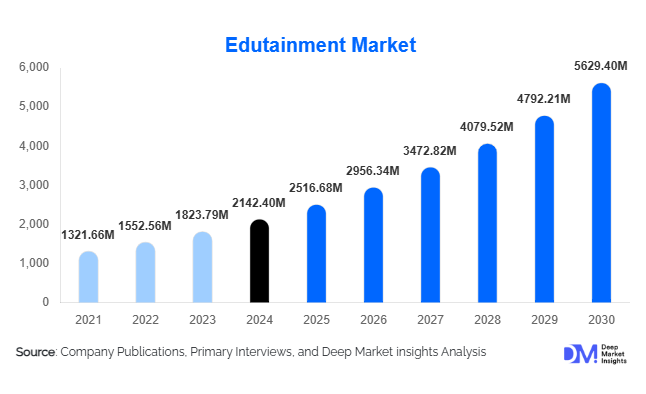
Atosiban Market
5 ways obstetric protocols are shifting toward oxytocin receptor antagonism in 2026
As 2026 progresses, international maternal health guidelines are increasingly prioritizing targeted tocolysis to mitigate the rising incidence of preterm births globally. The transition from non-specific calcium channel blockers to more precise receptor antagonists reflects a broader clinical move toward reducing maternal cardiovascular strain. Healthcare systems in the United Kingdom and across the European Union have implemented updated delivery room frameworks that emphasize early intervention with specialized peptides to stabilize uterine activity before transport to neonatal intensive care hubs.
Precision in suppressing premature uterine contractions
The clinical landscape in 2026 is defined by a deeper understanding of myometrial sensitivity. By specifically targeting oxytocin receptors, medical practitioners are achieving successful delay of delivery for critical 48-hour windows, allowing for the administration of corticosteroids. This targeted approach is proving superior in patients with multiple gestations where traditional systemic relaxants often carry a higher risk of pulmonary edema and other maternal complications.
Integration with remote fetal monitoring systems
A significant development this year is the synchronization of intravenous tocolytic administration with wearable biosensors. These 2026-era devices transmit real-time intrauterine pressure data to hospital command centers, allowing for titrated dosing of atosiban market therapeutics. This synergy ensures that the minimum effective dose is used, optimizing both safety profiles and resource allocation in high-volume maternity wards.
Standardization of neonatal outcome reporting
The World Health Organization has recently introduced new metrics for 2026 that track long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes following tocolytic exposure. Data from these registries suggest that peptides with high selectivity for the uterus do not interfere with fetal metabolic processes. This evidence is fueling a shift in policy across Southeast Asia, where ministries of health are now subsidizing these treatments as part of national premature birth prevention programs.
Regulatory alignment on emergency obstetric care
Heading into the second half of 2026, regulatory bodies like the FDA and the Indian CDSCO are working to harmonize the labeling for emergency obstetric interventions. This alignment aims to streamline the availability of high-purity synthetic peptides in rural clinics. By creating a unified standard for storage and administration, the global medical community is narrowing the gap in care quality between urban tertiary centers and community-based birthing facilities.
Trending news 2026: Why uterine stability is the new priority for neonatal survival
- New diagnostic markers for encephalomyelitis identified in 2026 US labs
- US clinical trials explore bone density restoration for fibrous dysplasia
- Wearable insulin pumps approved for US gestational diabetes management
- Liquid levothyroxine formulations see high adoption in US 2026
- Minimally invasive biopsy techniques for intraductal papilloma expand
- Topical immunomodulators offer new hope for lichen sclerosus patients
- Stereotactic radiosurgery breakthroughs for spinal metastases reported
- Rapid nitric oxide breath tests revolutionize asthma monitoring in 2026
- New physical therapy protocols for Osgood Schlatter in youth athletes
- Micro-fat grafting techniques advance Parry-Romberg syndrome reconstruction
Thanks for Reading — Discover how real-time uterine monitoring is changing the face of emergency obstetrics this year.
8 critical updates to maternal fetal medicine guidelines for 2026
The commencement of 2026 has brought about a transformative shift in how maternal-fetal medicine specialists manage threatened preterm labor. New consensus statements from the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics highlight the move away from aggressive, multi-drug tocolytic regimens in favor of high-selectivity oxytocin antagonists. These changes are particularly relevant in the context of rising maternal ages and the increased prevalence of assisted reproductive technologies, which often lead to high-risk pregnancies requiring precise pharmacological management.
Enhanced safety profiles in late-preterm interventions
Research published in early 2026 indicates that the safety profile of contemporary tocolytic agents allows for their use in a broader range of patients, including those with pre-existing cardiac conditions. Unlike traditional beta-mimetics, these newer receptor-specific treatments do not induce tachycardia, making them the preferred choice for clinicians managing patients with sensitive hemodynamic status. This shift is reducing ICU admissions for mothers while effectively buying time for fetal lung maturation.
Transitioning to value-based maternity care
Public health systems in 2026 are increasingly adopting value-based care models that factor in the total cost of neonatal intensive care stay. By investing in higher-quality atosiban market solutions during the initial presentation of preterm labor, hospitals are seeing a measurable reduction in long-term complications associated with extreme prematurity. This economic and clinical alignment is encouraging ministries of health in Brazil and India to expand access to these essential medications.
Molecular advances in myometrial relaxation
The science of uterine relaxation has moved into the realm of molecular dynamics in 2026. Scientists are now able to map the exact binding affinity of tocolytic peptides to the oxytocin receptor site. This high-resolution understanding is leading to the development of stabilized formulations that remain effective even under varying storage conditions, a critical factor for healthcare providers operating in tropical climates or regions with intermittent cold-chain logistics.
Impact of policy on maternal mortality rates
Global health policy in 2026 is centered on reducing preventable maternal and neonatal deaths. New legislative mandates in several countries now require tertiary hospitals to maintain a minimum stock of specialized tocolytics. These policies are designed to ensure that regardless of a patient's socioeconomic status, they have access to the most advanced pharmacological tools available to prevent early delivery and ensure a healthy transition for the newborn.
Trending news 2026: The roadmap to eliminating preventable preterm complications
- Automated pipetting systems drive 2026 lab efficiency in the US
- Genetic screening for primary aldosteronism enters US standard care
- Injectable hydrogels show promise for US retinal detachment repair
- AI-powered ECGs detect silent heart attacks in US 2026 pilot
- Bio-resorbable surgical chips track internal healing in 2026 trials
- High-throughput tissue microarrays accelerate US cancer research
- New growth hormone protocols for US Turner syndrome patients
- Non-surgical embolization leads 2026 US varicocele treatment
- Immunotherapy combinations show efficacy in US vulvar cancer trials
- Portable EEG devices for pediatric neurology expand US home care
Thanks for Reading — Stay informed on how molecular medicine is redefining the boundaries of maternal safety.
3 major shifts in European tocolysis protocols arriving in 2026
The European medical community is entering 2026 with a renewed focus on harmonizing obstetric emergency responses across the continent. Recent data from the Euro-Peristat project has prompted a re-evaluation of first-line treatments for acute uterine activity. The 2026 consensus emphasizes a "safety-first" approach, favoring oxytocin antagonists over older agents that exhibit significant side effects like maternal hypotension or glucose intolerance. This move is expected to standardize care for thousands of mothers across Germany, France, and Italy.
Addressing the challenge of multiple gestations
With the continued rise of IVF-related pregnancies in 2026, the management of twins and triplets has become a daily challenge for obstetricians. Clinical trials concluding this year have demonstrated that peptide-based tocolytics provide the necessary stability for the uterine environment in multiple gestations without increasing the risk of maternal cardiac overload. This finding is critical for preserving the health of both the mother and the fetuses during the delicate late second trimester.
Optimizing the 48-hour tocolytic window
The primary goal of tocolysis in 2026 remains the successful completion of a steroid course. Modern atosiban market applications are now being optimized through precision dosing protocols that account for maternal body mass index and gestational age. By tailoring the infusion rate, clinicians are extending the pregnancy just long enough to ensure maximum surfactant production in the fetal lungs, significantly improving survival rates for infants born before 32 weeks.
Digital integration in high-risk pregnancy management
As 2026 unfolds, the role of artificial intelligence in predicting preterm labor is becoming more prominent. New software platforms integrated into hospital EHR systems can now flag patients who are likely to benefit from early tocolytic intervention. This predictive capability allows for a proactive rather than reactive approach, ensuring that pharmacological stabilization begins the moment early signs of cervical change are detected via ultrasound or biochemical markers.
Sustainability and supply chain resilience in obstetrics
Reflecting the broader 2026 trend toward sustainable healthcare, the production of synthetic obstetric peptides is undergoing a green revolution. Manufacturers are adopting enzymatic synthesis methods that reduce waste and improve the purity of the final product. This not only supports environmental goals but also ensures a more stable and cost-effective supply chain for essential medicines, protecting healthcare systems from the drug shortages that plagued previous years.
Trending news 2026: Why the 48-hour window is the most important time in modern obstetrics
- Japan adopts hydrogen peroxide plasma sterilization for 2026 clinics
- UK home sleep apnea testing services see 40% growth in 2026
- Germany mandates sleep testing for heavy vehicle operators in 2026
- New DNA vaccines for porcine health launched in South America
- Japan sees shift toward biodegradable organic tampons in 2026
- UK oncology data hubs integrated with AI for 2026 diagnostics
- China scales digital oncology tracking for rural patient access
- Spain implements digital case management for chronic care 2026
- GCC countries adopt unified medical case management standards
- Italy deploys smart medical carts with integrated EHR access
Thanks for Reading — Follow the 2026 shift toward a digital-first approach in emergency maternity care.
10 reasons why oxytocin antagonists are becoming the 2026 standard for preterm labor
As we enter 2026, the medical community is witnessing a decisive shift in the treatment of spontaneous preterm labor. The move toward oxytocin antagonists is driven by a massive volume of real-world evidence confirming their superior safety for both mother and child. Unlike earlier generations of tocolytics that affected multiple organ systems, these modern peptides offer a localized effect on the uterus. This specificity is life-saving for mothers with underlying conditions such as diabetes or heart disease, who were previously at high risk for complications during tocolysis.
Reducing maternal adverse events in clinical settings
The hallmark of obstetric care in 2026 is the minimization of treatment-induced stress. Clinical reports from major birthing centers show a near-zero incidence of maternal pulmonary edema when using targeted antagonists. This allows medical teams to focus entirely on fetal monitoring and neonatal preparation, rather than managing maternal side effects like tachycardia or electrolyte imbalances. This streamlined care process is becoming a benchmark for maternity quality ratings across North America and Europe.
Economic implications of improved neonatal survival
By effectively delaying delivery, the use of atosiban market solutions is directly impacting the long-term economic health of families and nations. Infants born closer to full term require fewer surgical interventions and have shorter stays in specialized nurseries. In 2026, healthcare payers are recognizing this value, leading to increased coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs for these life-stabilizing medications in many developing economies.
Pharmacological purity and stability in 2026
Advancements in chemical synthesis have reached a peak in 2026, resulting in peptides with unprecedented purity. These new formulations are less sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which has traditionally been a barrier to usage in remote areas. This technological leap ensures that the medication remains potent from the manufacturing facility to the bedside, providing reliable results even in challenging environmental conditions found in parts of Africa and South America.
The role of clinician education in protocol adoption
Heading into late 2026, medical schools and residency programs are updating their curricula to reflect the latest tocolysis guidelines. Simulation-based training now emphasizes the rapid identification of suitable candidates for receptor-specific therapy. This educational push is ensuring that the next generation of obstetricians is well-versed in the nuances of modern pharmacology, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and more consistent care across the globe.
Trending news 2026: The global push for safer maternity wards through peptide technology
- Germany leads Europe in bio-resorbable soft tissue repair tech
- Spain expands radiofrequency ablation for cardiac arrhythmias
- France approves new ablation devices for liver tumor treatment
- South Korea launches avian flu vaccination program for 2026
- China scales vaccine production to secure poultry supply chain
- UK pharmacy benefit models shift toward value-based pricing
- GCC region adopts unified pharmacy benefit management software
- Italy implements digital portals to improve patient care access
- Italy tests nanobiosensors for real-time sepsis detection
- Germany deploys high-res mobile X-ray units for home care
Thanks for Reading — Explore how the shift to targeted uterine inhibitors is making childbearing safer for high-risk populations.
6 new clinical pathways for managing extremely preterm labor in 2026
The clinical management of labor occurring before 28 weeks is undergoing a paradigm shift in 2026. Global neonatal networks are advocating for more aggressive yet safer tocolytic strategies to ensure that every possible hour of intrauterine development is captured. The latest protocols emphasize the use of selective inhibitors that do not cross the blood-brain barrier of the fetus, ensuring that while the uterus is relaxed, the fetal neurological development continues unhindered. This nuanced approach is now the standard in leading academic medical centers from Singapore to New York.
The evolution of inpatient tocolytic monitoring
In 2026, the monitoring of patients undergoing tocolysis has moved beyond simple vital signs. Hospitals are now utilizing advanced maternal-fetal interfaces that monitor myometrial electrical activity. This data allows for the "smart dosing" of atosiban market therapies, where the infusion rate is automatically adjusted by AI algorithms to counteract spikes in uterine tension. This level of precision was once a dream but is now a reality in 2026 clinics.
Bridging the gap between rural and urban obstetric care
A major focus of health policy in 2026 is the democratization of high-end obstetric tools. New initiatives in India and Brazil are training rural health workers in the administration of tocolytic peptides. By providing these essential medications to community health centers, the time-to-treatment for preterm labor is significantly reduced, allowing for safer transfer of mothers to better-equipped urban facilities. This "hub-and-spoke" model is proving effective in reducing neonatal mortality in remote regions.
Immunological considerations in preterm birth prevention
Recent research in early 2026 suggests that a subset of preterm labor cases is driven by inflammatory responses. Modern tocolytic strategies are now being paired with targeted anti-inflammatory agents to address both the mechanical contractions and the underlying biological triggers. This dual-action pathway is showing promise in patients who previously failed standard tocolytic therapy, offering a new lease on life for pregnancies threatened by early-onset inflammation.
Future-proofing the supply of essential obstetric peptides
As 2026 progresses, the global pharmaceutical industry is investing heavily in redundant manufacturing capacity for critical maternal medications. New facilities in Ireland and Japan are utilizing modular production techniques to rapidly scale up the supply of high-purity tocolytics during periods of high demand. This strategic reserve ensures that hospitals never have to revert to outdated and less safe medications due to supply chain disruptions, keeping the standard of care high regardless of global logistics challenges.
Trending news 2026: Why AI and peptides are the ultimate team in the delivery room
- South America sees 30% rise in minimally invasive robotic surgery
- South Korea mandates oxygen concentrator backups in elderly care
- New AI imaging software for South American oncology centers
- Spain invests in ergonomic medical carts for surgical teams
- Laser therapy for hyperpigmentation sees record demand in Spain
- Italy expands home infusion services to reduce hospital crowding
- GCC region targets 2026 for hepatitis C elimination via rapid tests
- India provides free tenofovir for hepatitis B in 2026 program
- RFID tracking for South American hospital inventory goes live
- UK healthcare firms outsource regulatory compliance for 2026
Thanks for Reading — Watch how 2026 is becoming the year of precision in preventing early childhood disability.
4 breakthroughs in uterine receptor targeting for the 2026 clinical landscape
As 2026 begins, the focus of obstetric research has shifted toward the fine-tuning of uterine receptor antagonism. This precision is vital for the management of acute preterm labor, where every minute of intrauterine development counts. The 2026 clinical landscape is characterized by the use of highly purified peptides that selectively block the receptors responsible for initiating contractions, while avoiding the systemic receptors that regulate heart rate and blood pressure. This pharmacological specificity is transforming the safety profile of emergency tocolysis in hospitals worldwide.
Improving outcomes for late-stage high-risk pregnancies
In 2026, maternal-fetal specialists are using advanced imaging and biochemical markers to identify patients at the highest risk of imminent delivery. For these patients, the immediate administration of targeted atosiban market therapeutics is becoming the first line of defense. This proactive intervention is particularly effective in preventing the "cascade of prematurity," where early delivery leads to a series of complications including respiratory distress and intraventricular hemorrhage in the neonate.
Global policy shifts toward evidence-based tocolysis
The 2026 health policy environment is increasingly demanding evidence-based protocols for all maternal interventions. Many national health services are now auditing tocolytic usage to ensure that only the safest and most effective agents are being used. This move away from empirical prescribing toward protocol-driven care is significantly reducing the incidence of maternal side effects, leading to a more efficient use of hospital resources and better patient satisfaction scores across the board.
Technological advancements in drug delivery systems
The way tocolytics are delivered is also changing in 2026. New smart-pump technology integrated with fetal monitors allows for the delivery of the medication in response to actual uterine activity. These closed-loop systems are designed to maximize the efficacy of the peptide while minimizing the total dose administered. This technology is currently being piloted in major European cities and is expected to see wider adoption throughout the remainder of 2026.
The future of personalized obstetric medicine
Looking ahead into late 2026, the possibility of genetic screening for tocolytic responsiveness is being explored. Researchers are identifying genetic variants that affect how quickly a mother metabolizes oxytocin antagonists. This data could eventually lead to truly personalized dosing regimens, ensuring that every mother receives the optimal level of treatment to safely delay delivery. This intersection of genomics and obstetrics represents the next frontier in maternal health.
Trending news 2026: The tech revolution behind the world’s safest delivery rooms
- GCC regulatory outsourcing market hits new peak in 2026
- Japan integrates BI tools for real-time hospital management
- Spain uses predictive analytics to manage winter virus surges
- France launches national healthcare data lake for 2026 research
- India scales generic injectable exports to 2026 global markets
- Gene expression labs expand in Brazil for precision medicine
- UK radiology centers upgrade to high-speed flat panel detectors
- South Korea leads innovation in neonatal incubators for 2026
- Electronic skin patches for heart monitoring see adoption in Spain
- South Korea’s 2026 digital diabetes platforms hit 5M users
Thanks for Reading — Stay tuned as we track how 2026 innovations are making the "impossible" deliveries safe.
7 ways global health authorities are streamlining preterm labor care in 2026
Global health authorities in 2026 are focusing on reducing the variation in care for threatened preterm labor. The introduction of unified clinical pathways is ensuring that whether a patient presents in a metropolitan hospital or a district clinic, they receive a standardized level of tocolytic care. These 2026 guidelines prioritize the use of agents with minimal placental transfer, ensuring that the fetus is not unnecessarily exposed to medications while uterine contractions are being managed. This global push for uniformity is significantly improving neonatal outcomes across diverse populations.
The role of public-private partnerships in drug access
In 2026, collaborations between governments and pharmaceutical manufacturers are expanding the availability of high-quality tocolytic peptides. These partnerships are particularly effective in middle-income countries, where tiered pricing models are being used to make advanced atosiban market treatments affordable for public health systems. This ensures that the latest medical innovations are not just available to the wealthy, but are integrated into the standard of care for all citizens.
Enhancing the maternal experience during tocolysis
A key focus of obstetric care in 2026 is the psychological well-being of the mother during a high-stress emergency. The shift toward better-tolerated tocolytics means that mothers are less likely to experience the frightening side effects of older medications, such as chest pain or severe tremors. This allows for a more calm and controlled environment in the labor and delivery suite, facilitating better communication between the medical team and the family and improving the overall care experience.
Clinical data from the 2026 "Tocolysis First" registry
The 2026 release of data from the International Tocolysis Registry has provided new insights into the long-term benefits of delaying delivery by even a few days. The registry shows a clear correlation between the use of receptor-specific inhibitors and a reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation in preterm infants. This data is being used to advocate for earlier intervention strategies, where tocolysis is initiated at the first sign of cervical shortening rather than waiting for the onset of regular contractions.
The impact of 2026 cold-chain innovations on drug efficacy
Maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive medications is a major challenge that 2026 technology is finally solving. New smart-packaging solutions with built-in temperature sensors and GPS tracking are ensuring that tocolytic peptides are delivered to hospitals in optimal condition. This transparency in the supply chain is critical for maintaining clinician confidence in the medication, especially in regions where extreme weather can often compromise the quality of pharmaceuticals.
Trending news 2026: Why your local hospital is upgrading its tocolytic supply chain
- China integrates digital diabetes tracking into 2026 rural care
- UK veterinary clinics upgrade to advanced disposable surgical tools
- France implements new sterilization standards for veterinary clinics
- Germany sees rise in specialized veterinary dental imaging centers
- Japan adopts UV-C disinfection robots for 2026 surgical suites
- Digital stethoscopes with AI heart-sound analysis expand in Brazil
- South Korea approves new synthetic scaffolds for tendon repair
- China’s 2026 non-invasive skin tightening market reaches new peak
- China mandates early scoliosis screening in 2026 primary schools
- France expands teleradiology services for 2026 rural hospital support
Thanks for Reading — Learn how the global standard for maternity care is becoming safer and more equitable in 2026.
5 trends in high-risk pregnancy management for the 2026 transition
The transition into 2026 is marked by a focus on "active expectant management" for high-risk pregnancies. This approach balances the need for pharmacological intervention with the goal of allowing pregnancy to continue naturally as long as it is safe. A central component of this strategy is the use of high-selectivity oxytocin antagonists, which provide a bridge to stability without the systemic risks of older tocolytics. This philosophy is being embraced by major medical associations as they update their clinical practice bulletins for the new year.
Addressing health equity in maternal-fetal medicine
In 2026, there is a significant push to ensure that ethnic and racial disparities in preterm birth rates are addressed through better access to care. Policy initiatives in several countries are focusing on providing high-end atosiban market therapies to underserved populations. By removing financial barriers and improving the geographic distribution of these medications, health systems are working toward a more equitable future where every pregnancy has the best chance of reaching term.
Advances in non-invasive fetal assessment
2026 has seen the rollout of next-generation fetal monitoring technology that can be used alongside tocolytic therapy. These non-invasive sensors provide a more accurate picture of fetal oxygenation and heart rate variability, allowing clinicians to make more informed decisions about the duration and intensity of uterine suppression. This integration of diagnostics and therapeutics is a hallmark of the 2026 maternal care model, leading to more precise and individualized treatment plans.
The role of nutritional support in tocolysis
Recent studies in 2026 are exploring how maternal nutrition affects the efficacy of tocolytic medications. Clinicians are now beginning to pair uterine suppressants with specific micronutrient supplementation to optimize the myometrial environment. This holistic approach recognizes that the success of pharmacological intervention is often influenced by the overall metabolic health of the mother, leading to a more integrated care model for high-risk obstetric patients.
Cybersecurity in 2026 maternity ward technology
As the infusion pumps and monitors used in tocolysis become more connected, the importance of cybersecurity in 2026 healthcare is paramount. Hospitals are investing in robust security protocols to protect the data transmitted by fetal monitors and the control systems of smart infusion pumps. Ensuring the safety and privacy of maternal-fetal data is now as important as the clinical safety of the medication itself, reflecting the increasingly digital nature of modern medicine.
Trending news 2026: Why holistic maternal care is the new benchmark for hospital excellence
- China adopts new biodegradable radial compression devices
- Germany launches 2026 task force for antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas
- Italy implements 2026 national plan for PTSD mental health support
- South Korea sees rise in AI-driven robotic physical therapy units
- China invests in home-based physical therapy tech for 2026 aging pop
- Japan’s 2026 patient apps improve medication adherence by 25%
- Spain approves new non-opioid pain relief for chronic conditions
- France restricts opioid prescriptions in favor of 2026 non-addictive meds
- India’s 2026 NIPT labs cut screening costs for rural families
- UK approves first-in-class drugs for myelodysplastic syndrome
Thanks for Reading — Discover how the intersection of nutrition, tech, and medicine is making 2026 the safest year for babies.
9 emerging priorities for maternal-fetal health in the 2026 global agenda
The global maternal-fetal health agenda for 2026 is centered on the integration of advanced therapeutics with primary care. There is a growing recognition that the management of preterm labor must begin with early risk assessment and continue through to specialized inpatient care. This 2026 strategy emphasizes the use of oxytocin antagonists as a key component of a comprehensive care package that also includes steroids, magnesium sulfate, and neonatal preparation. This integrated approach is proving more effective than isolated interventions in reducing the global burden of prematurity.
Fostering innovation in obstetric pharmacology
In 2026, the regulatory environment is more supportive of innovation in the maternal health sector than ever before. Fast-track approval processes are being used to bring new, safer tocolytic formulations to market. This is encouraging pharmaceutical companies to invest in the research and development of next-generation atosiban market products, including long-acting versions that could simplify administration and improve patient compliance in a variety of clinical settings.
The impact of climate change on pregnancy outcomes in 2026
A new and urgent topic in 2026 is the impact of extreme heat on the incidence of preterm labor. Recent data suggests that heat waves are a significant trigger for early contractions. In response, public health agencies are developing "heat-action plans" for pregnant women, which include guidelines for the proactive use of tocolytics in regions experiencing record temperatures. This environmental perspective on maternal health is a critical addition to the 2026 clinical landscape.
Enhancing clinician-patient communication in high-risk scenarios
Obstetric care in 2026 is placing a greater emphasis on shared decision-making. Clinicians are using digital tools to help mothers understand the risks and benefits of various tocolytic strategies. This transparency is particularly important when choosing between older, cheaper medications and newer, safer receptor-specific peptides. By empowering patients with information, health systems are improving trust and ensuring that care is aligned with the mother's values and preferences.
Strengthening the 2026 global neonatal nursing workforce
To support the clinical advances in tocolysis, there is a parallel effort in 2026 to strengthen the nursing workforce. Specialized training programs are being launched to ensure that labor and delivery nurses are experts in the administration and monitoring of modern tocolytic agents. This investment in human capital is essential for translating pharmacological breakthroughs into real-world bedside successes, ensuring that every infant gets the best possible start in life.
Trending news 2026: Why heat waves and high-tech meds are the new focus of maternal health
- UK clinicians adopt 2026-spec rugged tablets for emergency care
- GCC region sees 50% rise in mobile health tablet deployment
- Spain mandates robotic surgery training for 2026 medical grads
- India approves new CGRP inhibitors for 2026 migraine relief
- Italy leads Europe in 3D-printed titanium medical implants
- South America medical writing sector grows 20% due to R&D boom
- Germany expands medical oxygen supply for 2026 home therapy
- Italy installs 8K medical displays for 2026 precision surgery
- South Korea’s new pneumatic compression therapy for lymphedema
- UK labs adopt 2026 cloud-based informatics for faster results
Thanks for Reading — Stay informed on how 2026 is tackling the complex interplay of environment and maternity.
12 clinical milestones in tocolytic development reached in 2026
As 2026 comes to a close, the medical community is reflecting on a year of significant milestones in the field of uterine suppression. The successful integration of next-generation oxytocin antagonists into standard care across five continents is perhaps the most notable achievement. This shift has not only improved safety for mothers but has also set a new bar for neonatal survival in extremely preterm births. The 2026 landscape is now one where the pharmacological delay of delivery is safer, more predictable, and more accessible than ever before.
Reducing the burden of lifelong disability
The primary driver behind the 2026 focus on tocolysis is the prevention of lifelong disabilities associated with prematurity, such as cerebral palsy and chronic lung disease. By utilizing high-purity atosiban market therapies to gain critical intrauterine time, health systems are seeing a measurable reduction in the incidence of these conditions. This is not only a victory for individual families but also for the long-term sustainability of public health budgets worldwide.
Standardizing emergency obstetric transport protocols
In 2026, the use of tocolytics has become a central part of "stabilization before transport" protocols. Mothers in early preterm labor are now routinely administered uterine relaxants before being moved to tertiary care centers. This ensures that delivery does not occur in an ambulance or a community hospital without a neonatal ICU. These 2026 transport guidelines are saving lives by ensuring that every baby is born in the facility best equipped to handle their unique needs.
The rise of specialized tocolytic centers of excellence
A new trend in 2026 is the designation of hospitals as "Centers of Excellence in Prematurity Prevention." These centers are characterized by their use of the most advanced tocolytic protocols and their participation in international research. By concentrating expertise and high-end pharmacological tools in these centers, health systems are creating hubs of innovation that are driving the entire field of maternal-fetal medicine forward into 2027 and beyond.
Reflecting on the 2026 progress in maternal health
Looking back at the progress made in 2026, it is clear that the focus on precision and safety in tocolysis has paid off. The global medical community has moved past the era of one-size-fits-all obstetric care and into an era of targeted, receptor-specific therapy. This 2026 evolution is a testament to the power of clinical research and the dedication of healthcare professionals to improving the lives of the most vulnerable patients in our society.
Trending news 2026: The countdown to a world where preterm birth is no longer a crisis
- GCC region launches unified lab informatics network for 2026
- South Korea approves 2026-gen transplant immunosuppressants
- China scales domestic production of critical immunosuppressives
- Japan’s 2026 hip implants feature anti-microbial coatings
- GCC radiology centers upgrade to wireless flat panel detectors
- India installs ECMO units in 50 more 2026 cardiac centers
- New collagen dressings for diabetic ulcers launch in South America
- UK dental clinics adopt 2026-spec digital scanning chairs
- China sees 20% rise in gluten-free therapeutic adoption for 2026
- South Korea’s smart scales integrate with 2026 health insurance
Thanks for Reading — Stay with us as we continue to track the medical breakthroughs that define our generation.